How Background Verification Works in India (Step-by-Step)
Background verification in India is no longer a simple checkbox in the hiring process. As companies scale, work remotely, and handle sensitive information, verifying every candidate’s credentials has become a crucial operational safeguard. Understanding how the process works step-by-step helps HR teams, recruiters, and decision-makers plan hiring efficiently while minimizing risk.
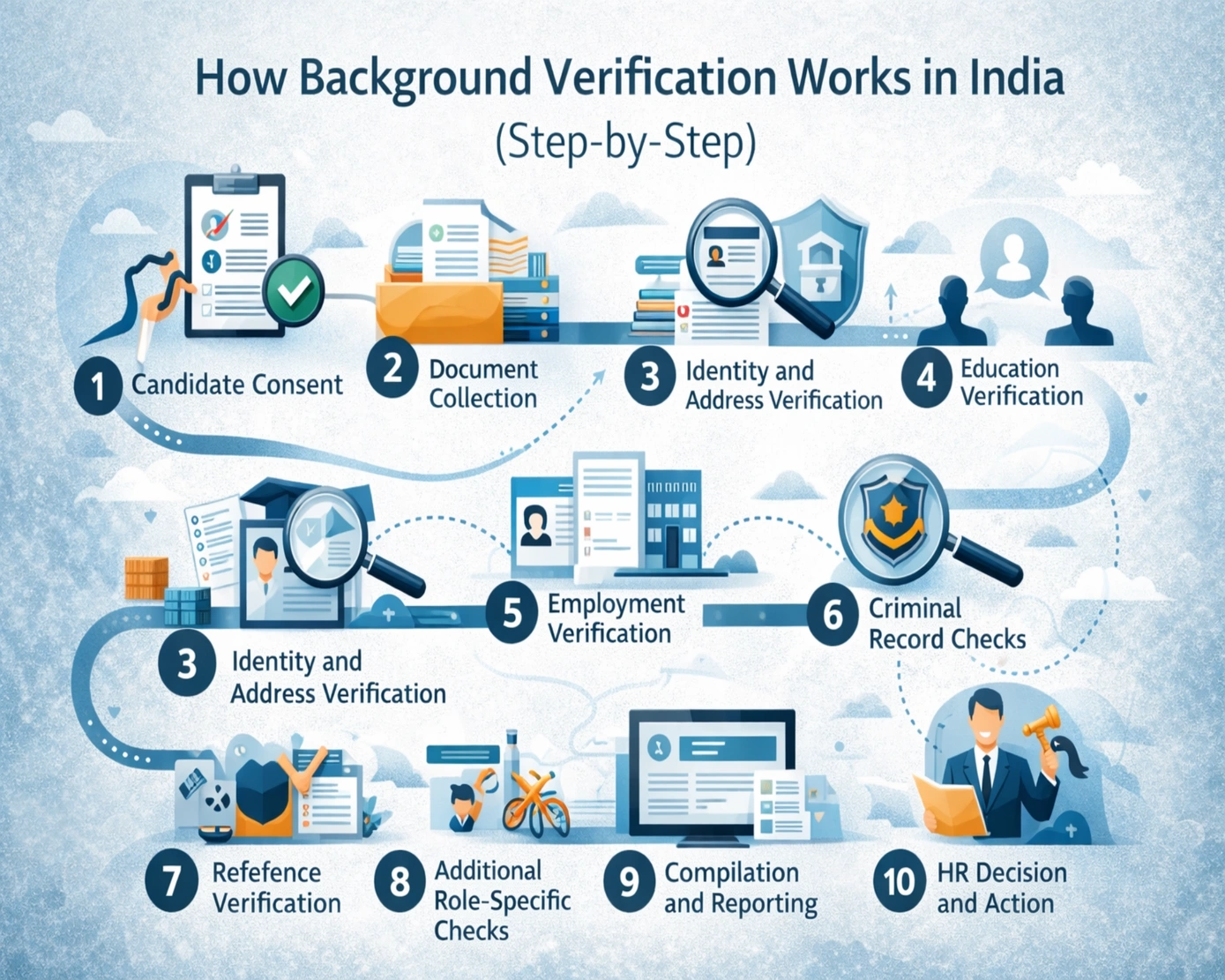
Step 1: Candidate Consent
The process begins with formal consent. Before any verification starts, candidates are required to give written permission. This is not only a legal requirement under India’s data protection norms but also a critical step for transparency and fairness. It ensures that the candidate understands the verification scope, the types of documents required, and the potential outcomes.
Step 2: Document Collection
Once consent is obtained, candidates submit relevant documents. These usually include identity proofs (Aadhaar, PAN, passport), address proof, educational certificates, employment records, and any additional role-specific documents such as medical reports or professional certifications. Accurate document submission at this stage determines the efficiency of the verification process.
Step 3: Identity and Address Verification
Verification begins with confirming the candidate’s identity and address. Government databases, utility bills, and field verification processes are used to ensure authenticity. This step reduces risks such as identity fraud, impersonation, and fake residential claims.
Step 4: Education Verification
Education verification confirms that the degrees, diplomas, or professional certifications presented by the candidate are legitimate and issued by recognized institutions. Verification agencies contact colleges, universities, and certification bodies to validate academic claims. In regulated or technical roles, this step is particularly critical as it directly impacts job performance and compliance.
Step 5: Employment Verification
Employment verification ensures that the candidate’s previous work history is accurate. HR teams or verification agencies confirm past job roles, tenure, and reasons for leaving with former employers. This prevents inflated experience claims, fake work histories, or undisclosed concurrent employment.
Step 6: Criminal Record Checks
Criminal background checks are performed to identify any past or ongoing legal issues. Police records, court databases, and sanction lists are scanned to ensure workplace safety and legal compliance. Roles with financial responsibility, public interaction, or security access require stringent criminal verification.
Step 7: Reference Verification
Reference checks provide insight into the candidate’s behavior, work ethic, and cultural fit. Previous managers, colleagues, or professional contacts are interviewed to gain a qualitative understanding of the candidate beyond documents.
Step 8: Additional Role-Specific Checks
Depending on the role, additional verifications may be conducted. These can include drug tests, health screenings, global compliance checks, or moonlighting verification. These checks help protect the organization from specific operational and regulatory risks.
Step 9: Compilation and Reporting
All verification findings are compiled into a detailed, audit-ready report. HR teams review this report before finalizing the hiring decision. The report highlights discrepancies, risks, and areas that require clarification.
Step 10: HR Decision and Action
Based on the findings, HR teams make informed decisions. Minor discrepancies may be clarified with the candidate, while major discrepancies, such as falsified education or undisclosed criminal history, can influence the offer or onboarding decision.
Final Thought
Background verification is not a bureaucratic formality. It is a systematic, evidence-driven process that protects companies from hiring risk, legal exposure, and operational failure. Understanding the steps involved allows HR teams, recruiters, and leaders to implement verification efficiently, without slowing down hiring or compromising safety.

Leave a comments